Fiber Glass Fabric
UNIDIRECTIONAL FABRIC
Unidirectional (UD) Fabric is a type of technical textile where nearly all of the fibers are oriented in a single, parallel direction—typically along the length (warp). Unlike woven fabrics, which have fibers interlaced in two directions (0∘ and 90∘), UD fabric utilizes stitching or a binder to hold the straight, non-crimped fibers together. This construction is engineered to deliver maximum strength and stiffness precisely where it’s needed, along the 0∘ axis.
Key Features and Performance Benefits
Maximum Longitudinal Strength: Because the load is transferred directly through straight fibers, UD fabric provides the highest possible tensile strength and stiffness along the fiber’s axis compared to any other reinforcement format (like woven or chopped strand mat).
Zero Crimp: The fibers are not crimped (bent) as they are in a woven fabric. This eliminates strength reduction caused by fiber straightening under load, maximizing mechanical properties.
Targeted Reinforcement: Ideal for applications where the primary stresses are known and act predominantly in one direction, allowing for highly efficient material usage and weight savings.
Excellent Fiber-to-Resin Ratio: The flat, straight arrangement of the fibers allows for superior wet-out and a higher fiber volume fraction in the final composite, leading to a stronger, lighter part.
Typical Applications
UD fabrics are critical components in high-performance composites across various industries, including:
Aerospace: Reinforcement for spars, booms, and wing skins where directional strength is paramount.
Wind Energy: Primary reinforcement in the root and spar caps of large wind turbine blades to handle immense bending loads.Marine: Localized strengthening of masts, keels, and high-stress areas in performance yachts.
Sporting Goods: High-strength layers in items like bicycle frames, golf shafts, and surfboards to control flex and increase power transfer.
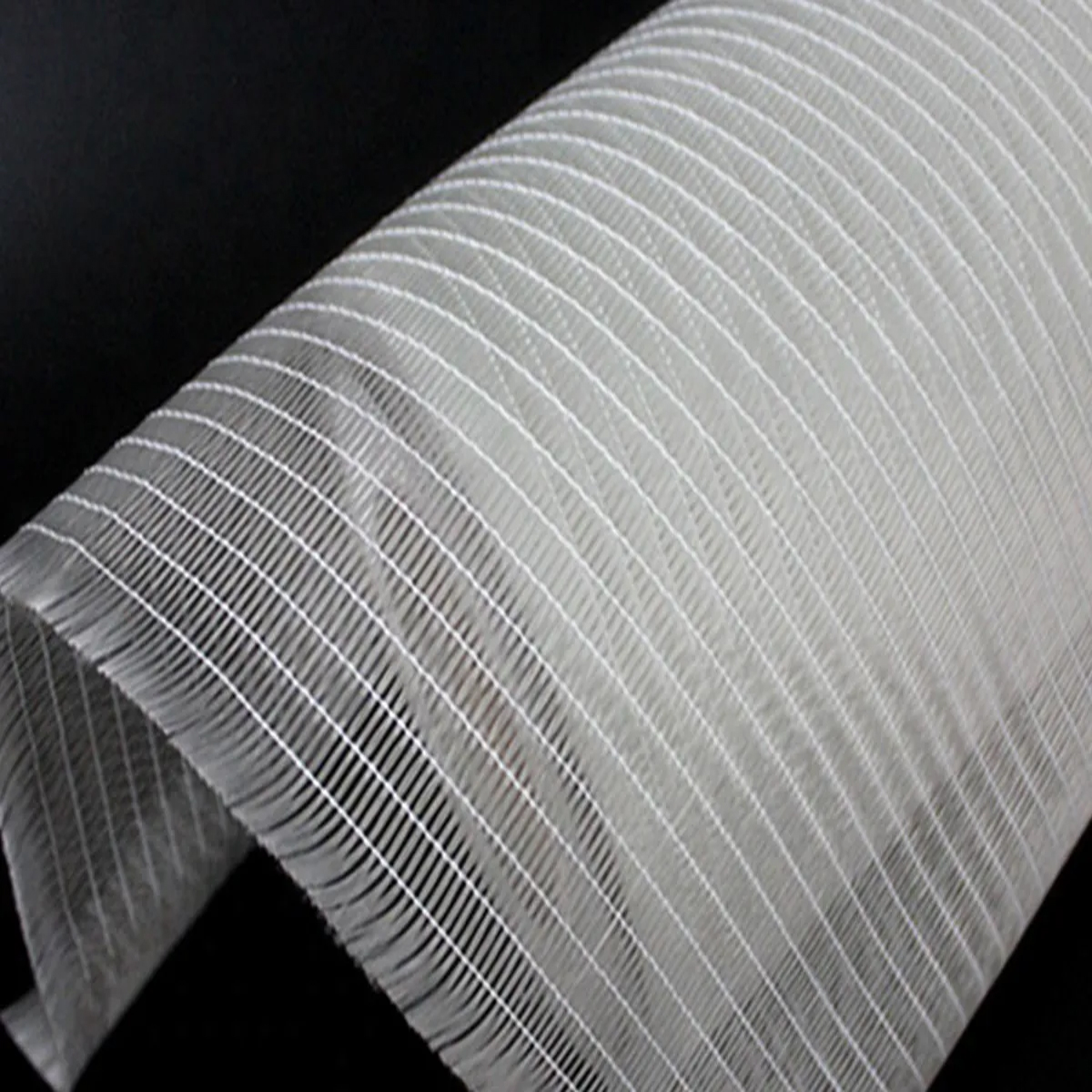

BIAXIAL FIBER GLASS FABRIC
Biaxial Fiberglass Fabric is a highly efficient non-crimp fabric (NCF) composed of continuous glass rovings stitched together at two specific orientations, typically +45∘ and −45∘ to the warp (lengthwise) direction. Unlike traditional woven roving, the fibers in biaxial fabrics lie completely straight and are held together by light stitching, eliminating the crimp (bend) found in woven materials. This straight alignment ensures superior translation of fiber strength into the laminate, providing maximum mechanical properties and faster wet-out with resin.
Key Advantages and Features Optimal Strength Translation: With fibers lying straight and flat, the fabric delivers up to 30% better mechanical properties (tensile and flexural strength) compared to woven materials of the same weight.
-
Targeted Reinforcement: The ±45∘ orientation is specifically engineered to handle torsional (twisting) and shear stresses, making it ideal for diagonal loads often encountered in boat hulls, spars, and beams.
-
Fast Resin Wet-Out: The open, non-crimped structure allows resin to penetrate quickly and thoroughly, leading to faster lay-up times and a more consistent, void-free laminate.
-
Reduced Weight: Provides the necessary strength with less material and resin compared to conventional reinforcement, resulting in a lighter overall part.
-
Versatile Compatibility: Can be stitched to a variety of backings, such as chopped strand mat (CSM) or veil, to create combo-mats, enhancing bulk and ease of use in hand lay-up and infusion processes.
Typical Applications
Due to its high performance and specific fiber orientation, Biaxial Fiberglass Fabric is the material of choice for demanding composite applications, including:
-
Marine Construction: Reinforcement of boat hulls, decks, transoms, and bulkheads to resist high torsional loads.
-
Wind Energy: Fabrication of wind turbine blades and nacelles requiring targeted stiffness and shear resistance.
-
Automotive/Transportation: Structural components and chassis parts where lightweight strength is critical.
-
Industrial Components: Manufacturing of high-strength tanks, pipes, and beams for corrosive environments.
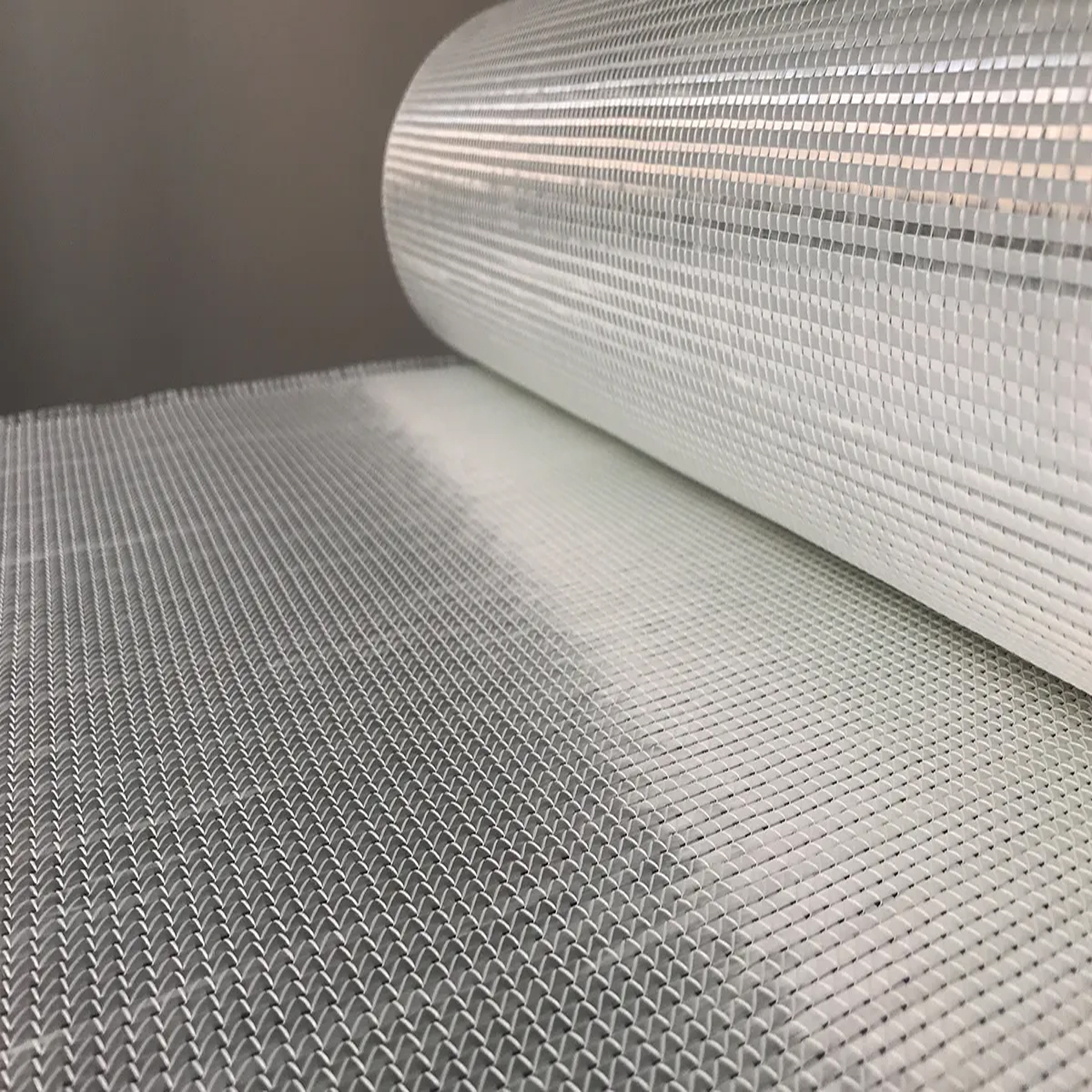

TRIAXIAL FIBER GLASS FABRIC
Our Triaxial Fiber Glass Fabric is an advanced, non-crimp fabric (NCF) that provides superior multi-directional strength compared to traditional woven or biaxial materials. This reinforcement features three sets of fibers oriented at 0∘, +45∘, and −45∘ (or 0∘, +60∘, and −60∘ for some applications), mechanically stitched together. This unique lay-up is ideal for applications requiring exceptional resistance to torsional stress, shear loads, and fatigue.
Key Features & Benefits
Exceptional Shear and Torsional Strength: The ± angle fibers are specifically engineered to handle the complex forces (like twisting and racking) that straight-woven fabrics struggle with, creating a more durable and rigid composite.
Optimal Fiber Placement: Because the fibers are stitched and not crimped, they remain straighter. This allows for maximum load translation and results in a stronger part per unit of weight compared to woven roving.
High Lay-up Speed: The wide, stable rolls allow for faster material handling and lay-up in large molds, reducing labor time in manufacturing.
Excellent Wet-Out: The open, non-woven structure promotes rapid and complete resin saturation (wet-out), minimizing air entrapment and ensuring a high-quality, void-free laminate.
Versatile Process Compatibility: It is perfectly suited for high-performance processes such as Resin Infusion (RI), Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding (VARTM), and Hand Lay-up.
Ideal Applications
Triaxial fabric is the go-to choice for composite parts where high stiffness, strength, and fatigue resistance are critical:
Marine Industry: High-performance boat hulls, decks, and bulkheads where wave impact and twisting forces are significant.
Wind Energy: Critical components in wind turbine blades and nacelles that must withstand constant flexing and wind loads.
Automotive/Transportation: Structural parts, chassis components, and body panels requiring a high strength-to-weight ratio.
Industrial/Construction: Beams, spars, and other load-bearing structural parts for infrastructure projects.
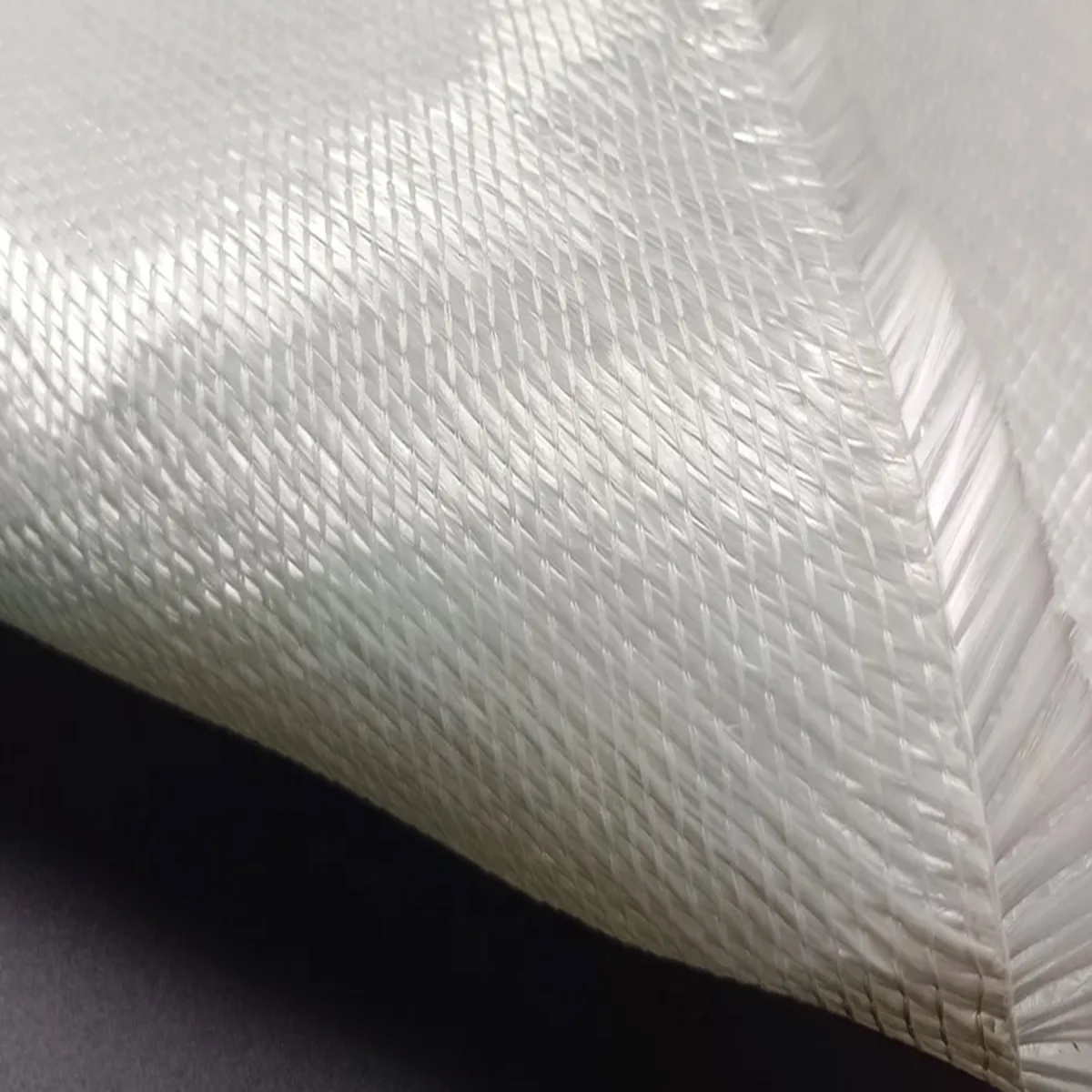

QUADRIAXIAL FIBER GLASS FABRIC
Quadriaxial Fabric is a high-performance non-crimp fabric (NCF) composed of four layers of unidirectional fiberglass rovings stitched together. These layers are precisely oriented at 0∘, +45∘, 90∘, and −45∘
(or vice versa), providing reinforcement in four directions simultaneously. This unique structure ensures exceptional load distribution and mechanical properties in composite structures.
Key Features & Advantages
Multiaxial Strength: Delivers superior strength and stiffness compared to woven fabrics, offering high resistance to torsional and bending loads.
High Fiber Content: The non-crimp structure allows for maximum fiber loading with minimal resin consumption, resulting in a lighter and stronger laminate.
Rapid Wet-Out: The stitched construction facilitates fast and efficient resin flow, making it ideal for processes like vacuum infusion, RTM (Resin Transfer Molding), and hand lay-up.
Controlled Thickness: Provides a highly uniform and predictable laminate thickness, improving the consistency of manufactured parts.
Reduced Print-Through: Minimizes the transfer of the fabric pattern onto the surface of the finished part, resulting in a better cosmetic finish.
Ideal Applications
The balanced, four-direction reinforcement of Quadriaxial Fabric makes it indispensable for applications requiring high structural integrity and durability:
Marine Industry: Large boat hulls, decks, masts, and bulkheads where impact and bending resistance are critical.
Wind Energy: Manufacturing of large wind turbine blades to handle dynamic forces and fatigue.
Automotive/Transportation: Structural parts, chassis components, and body panels requiring high strength-to-weight ratios.
Civil Engineering: Components for bridges, beams, and structural reinforcements in construction.
Industrial: High-strength tanks and pressure vessels for industrial applications.
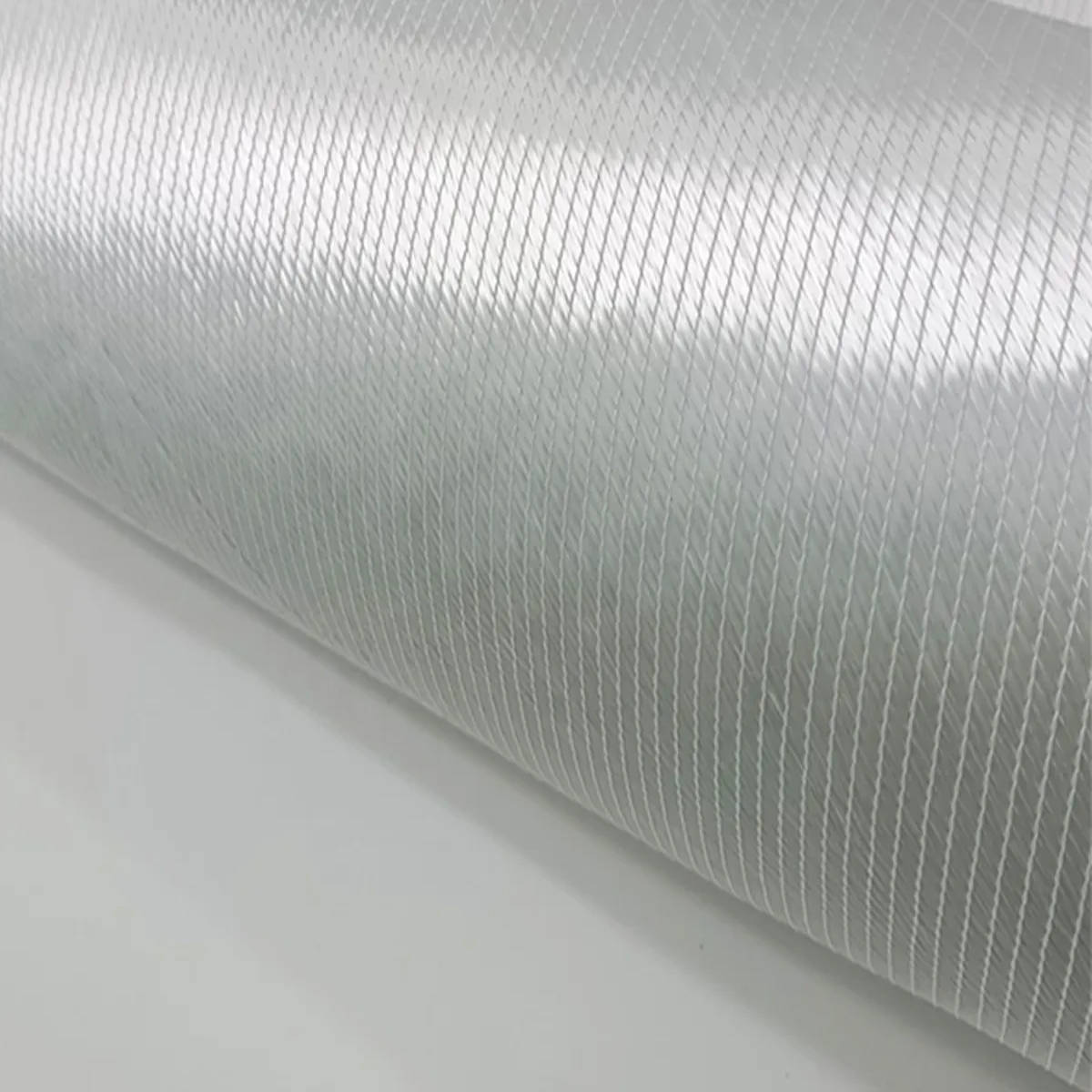

WOVEN ROVING
Woven Roving is a heavy-duty fiberglass fabric made by interweaving continuous glass fiber rovings (bundles of filaments). It’s designed to provide maximum strength and stiffness to composite laminates, making it an essential material for structural applications. It is typically used in conjunction with Chopped Strand Mat (CSM) or other light reinforcement to build up laminate thickness rapidly while ensuring high mechanical performance.
Key Features and Advantages
Exceptional Mechanical Strength: Due to the woven nature of the thick rovings, it offers superior tensile and flexural strength in the plane of the fabric (both warp and weft directions).
Rapid Thickness Buildup: The heavy weight of the fabric allows laminators to achieve desired thickness with fewer layers, saving time and resin.
Good Resin Wet-Out: Despite its coarse texture, Woven Roving is designed to allow resin (Polyester, Vinyl Ester, or Epoxy) to penetrate and wet-out the fiber bundles effectively.
Dimensional Stability: The woven construction provides a stable fabric that is easy to handle and remains in place during lamination.
Versatile Weight Range: Available in various weights (e.g., 18 oz/yd2 to 36 oz/yd2) to suit different strength and thickness requirements.
Ideal Applications
Woven Roving is the reinforcement of choice for products that demand a high strength-to-weight ratio and robust structural integrity.
Marine Industry: Construction of large boat hulls, decks, masts, and bulkheads.
Automotive/Transportation: Manufacturing of structural components, chassis parts, and body panels.
Storage Tanks and Pipes: Reinforcement for large chemical storage tanks and high-pressure pipes.
General Structural Composites: Beams, columns, and other load-bearing FRP structures.
Mold Making: Creating durable and rigid master molds for production parts.